Antares Cleaning Solutions
Your go-to source for cleaning tips and industry insights.
Is Your Smart Contract a Fair Game? Discover the Hidden Biases
Uncover the hidden biases in smart contracts! Is your blockchain game as fair as you think? Dive in to find out!
Unraveling Smart Contract Fairness: Key Factors to Consider
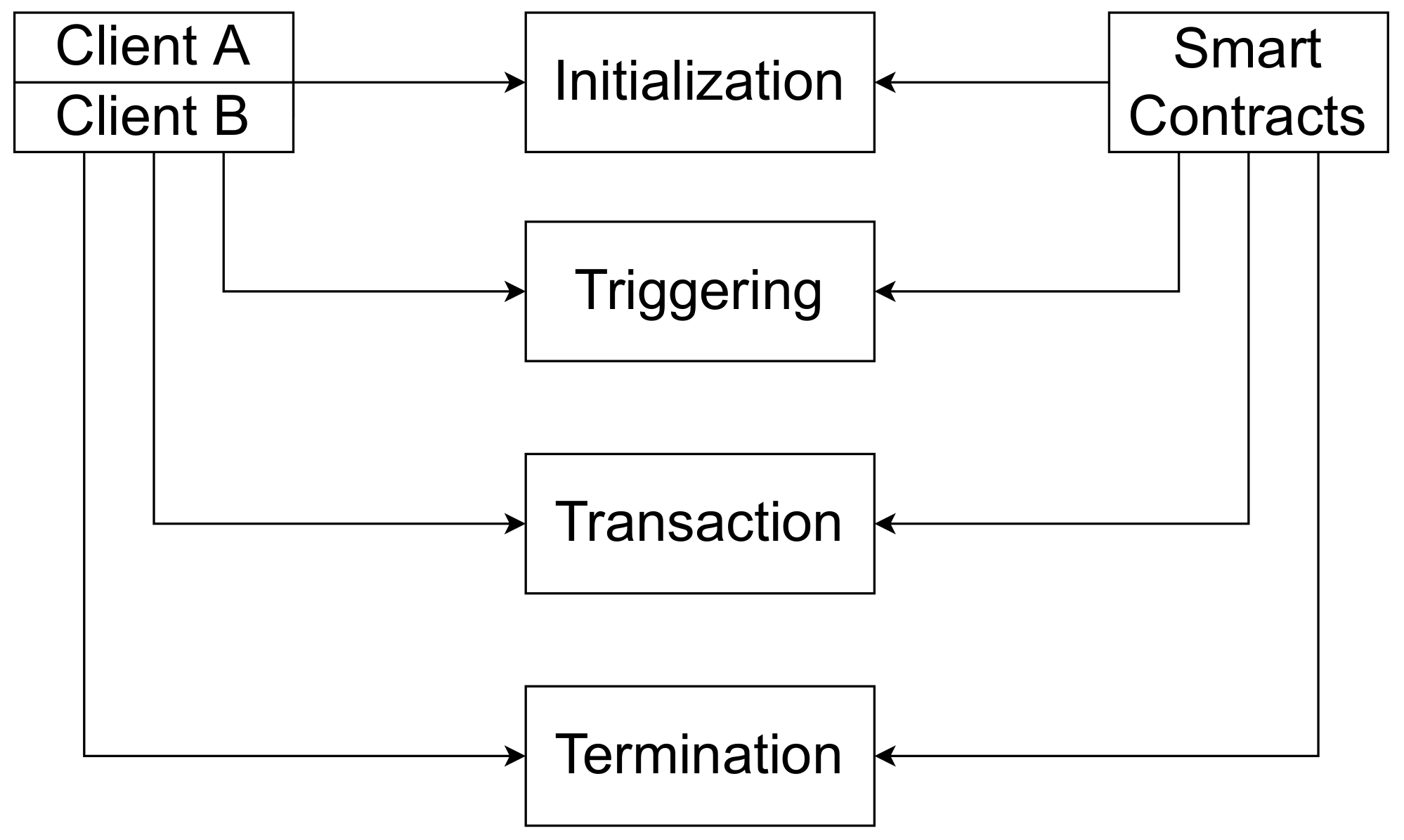
Smart contracts have revolutionized the landscape of decentralized applications, yet their fairness remains a pivotal concern for developers and users alike. When assessing the fairness of a smart contract, several critical factors come into play. First, the code transparency ensures that the logic of the contract is open for scrutiny, allowing users to verify the contract's functions and any terms laid out within. This transparency minimizes the risk of malicious intent and fosters trust among users. Additionally, it is essential to consider the incentive alignment of all parties involved. Properly aligning incentives helps prevent any party from exploiting the smart contract's outcomes for their own gain, ensuring equity in the process.
Furthermore, the oracle reliability is another key factor in achieving smart contract fairness. Oracles are responsible for providing real-world data to the blockchain, and if these are compromised or inaccurate, it can lead to unfair outcomes. Ensuring that oracles are trustworthy and have multiple data sources can mitigate such risks. Moreover, auditing plays a vital role in maintaining fairness in smart contracts. Regular audits by third-party professionals can identify vulnerabilities or biases in the contract's code before they lead to exploitations or disputes. In summary, fostering smart contract fairness requires a multifaceted approach that considers transparency, alignment of incentives, oracle reliability, and thorough auditing practices.
Counter-Strike is a highly popular team-based first-person shooter that has captivated gamers since its release. Players can engage in intense firefights, strategize with teammates, and compete in various game modes. If you're looking to enhance your gaming experience, check out the bc.game promo code for some exciting bonuses!
Are Your Smart Contracts Truly Trustworthy? Identifying Hidden Biases
The rise of blockchain technology has brought smart contracts to the forefront, promising greater transparency and trust in digital agreements. However, just because these contracts are coded to be automated and self-executing doesn't guarantee their **trustworthiness**. Identifying hidden biases in the design and implementation of smart contracts is essential. Developers may unintentionally embed their own biases through choices in algorithms, data selection, or the platforms they choose. As a result, understanding the underlying logic of smart contracts and conducting thorough audits can help uncover these biases and address potential weaknesses.
Moreover, the trustworthiness of smart contracts is not solely dependent on their technical execution. Legal and social contexts also play a critical role. Identifying hidden biases means scrutinizing not only the code itself but also the intentions behind it and the stakeholders involved. For example, a smart contract developed for a financial service may unfairly favor one party if not carefully reviewed. This highlights the need for ongoing scrutiny and collaboration among stakeholders to ensure that smart contracts serve their intended purpose without unintended prejudice.
What Makes a Smart Contract Fair? Exploring Common Pitfalls
In the realm of blockchain technology, smart contracts are hailed for their potential to automate and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries. However, the fairness of a smart contract is contingent upon clear and transparent coding, as well as a thorough understanding of its underlying logic. A contract that is poorly designed or ambiguously worded can lead to unintended consequences, often disadvantaging one party. To ensure fairness, developers must adhere to established best practices, such as conducting thorough audits and using well-tested templates. This minimizes the risk of quirks that could result in exploitation or unfair outcomes.
Common pitfalls in smart contracts can stem from algorithmic bias or a lack of inclusivity in their design. For example, if a smart contract is programmed based on skewed data sets, it may inadvertently favor certain outcomes or user profiles, creating an imbalanced playing field. To combat this, developers should actively seek feedback from diverse stakeholder groups and implement mechanisms for regular updates in response to real-world changes. Only through continuous evaluation and community involvement can smart contracts aspire to achieve true fairness, thereby fostering trust and wider adoption in the blockchain ecosystem.